12.4 Transforms
The AffineTransform
class can transform a shape (or coordinate system) by translating,
scaling, rotating, or shearing it, using any combination of these
individual transformation types. Figure 12-5
illustrates the results of various types of coordinate-system
transformations on the appearance of one shape, drawn multiple times.
Example 12-7 shows the Java code that generates the
figure.
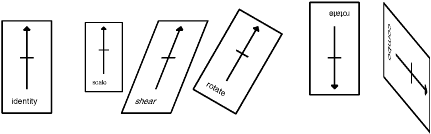
An affine transformation is a linear
transformation that has two important properties: all straight lines
remain straight, and all parallel lines remain parallel. The
AffineTransform class can perform a great variety
of transformations, but it can't produce nonlinear
effects, such as distorting a figure as through a fisheye lens. That
kind of effect can be achieved only with image-processing techniques.
For a further discussion of transformations and the linear algebra
behind the AffineTransform class, see Chapter 4 of Java Foundation Classes in a
Nutshell.
Example 12-7. Transforms.java
package je3.graphics;
import java.awt.*;
import java.awt.geom.*;
/** A demonstration of Java2D transformations */
public class Transforms implements GraphicsExample {
public String getName( ) { return "Transforms"; } // From GraphicsExample
public int getWidth( ) { return 750; } // From GraphicsExample
public int getHeight( ) { return 250; } // From GraphicsExample
Shape shape; // The shape to draw
AffineTransform[ ] transforms; // The ways to transform it
String[ ] transformLabels; // Labels for each transform
/**
* This constructor sets up the Shape and AffineTransform objects we need
**/
public Transforms( ) {
GeneralPath path = new GeneralPath( ); // Create a shape to draw
path.append(new Line2D.Float(0.0f, 0.0f, 0.0f, 100.0f), false);
path.append(new Line2D.Float(-10.0f, 50.0f, 10.0f, 50.0f), false);
path.append(new Polygon(new int[ ] { -5, 0, 5 },
new int[ ] { 5, 0, 5 }, 3), false);
this.shape = path; // Remember this shape
// Set up some transforms to alter the shape
this.transforms = new AffineTransform[6];
// 1) the identity transform
transforms[0] = new AffineTransform( );
// 2) A scale tranform: 3/4 size
transforms[1] = AffineTransform.getScaleInstance(0.75, 0.75);
// 3) A shearing transform
transforms[2] = AffineTransform.getShearInstance(-0.4, 0.0);
// 4) A 30 degree clockwise rotation about the origin of the shape
transforms[3] = AffineTransform.getRotateInstance(Math.PI*2/12);
// 5) A 180 degree rotation about the midpoint of the shape
transforms[4] = AffineTransform.getRotateInstance(Math.PI, 0.0, 50.0);
// 6) A combination transform
transforms[5] = AffineTransform.getScaleInstance(0.5, 1.5);
transforms[5].shear(0.0, 0.4);
transforms[5].rotate(Math.PI/2, 0.0, 50.0); // 90 degrees
// Define names for the transforms
transformLabels = new String[ ] {
"identity", "scale", "shear", "rotate", "rotate", "combo"
};
}
/** Draw the defined shape and label, using each transform */
public void draw(Graphics2D g, Component c) {
// Define basic drawing attributes
g.setColor(Color.black); // black
g.setStroke(new BasicStroke(2.0f, BasicStroke.CAP_SQUARE, // 2-pixel
BasicStroke.JOIN_BEVEL));
g.setRenderingHint(RenderingHints.KEY_ANTIALIASING, // antialias
RenderingHints.VALUE_ANTIALIAS_ON);
// Now draw the shape once using each of the transforms we've defined
for(int i = 0; i < transforms.length; i++) {
AffineTransform save = g.getTransform( ); // save current state
g.translate(i*125 + 50, 50); // move origin
g.transform(transforms[i]); // apply transform
g.draw(shape); // draw shape
g.drawString(transformLabels[i], -25, 125); // draw label
g.drawRect(-40, -10, 80, 150); // draw box
g.setTransform(save); // restore transform
}
}
}
|
